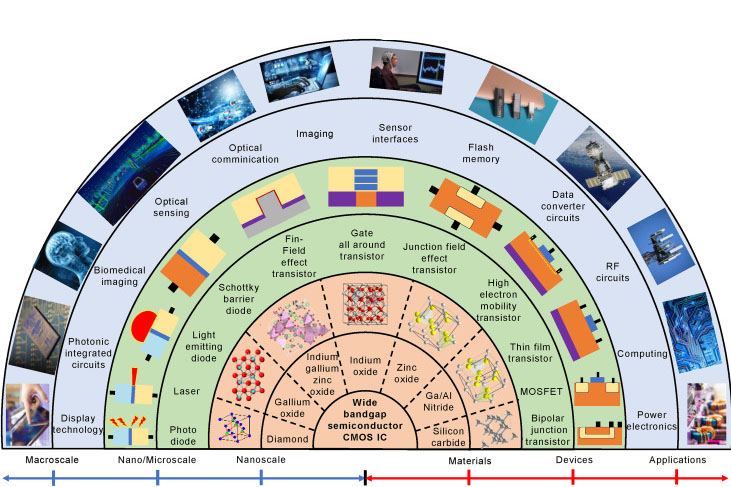
List of Gallium Compounds in Electronics
Gallium compounds are essential materials in the field of electronics. Notable gallium compounds, such as Gallium Arsenide (GaAs), Gallium Nitride (GaN), and Gallium Oxide (Ga₂O₃), are widely used in a variety of specialized applications due to their ability to perform efficiently in harsh environments, high frequencies, and extreme temperatures. We will discuss the key gallium compounds, their properties, uses, and the future role they play in advanced electronics.

[1]
1. Gallium Arsenide (GaAs)
Gallium Arsenide (GaAs) is an III-V compound semiconductor made of gallium and arsenic. It has a high electron mobility and a direct bandgap of about 1.42 eV, which makes it very suitable for applications that require fast switching speeds and effective light emission. Its thermal conductivity is also higher than that of silicon, hence helping in heat dissipation in high-power applications. It also has a high saturation velocity, allowing it to perform well at high frequency and high-speed circuits.
Applications of GaAs include high-speed electronic devices, such as RF amplifiers, microwave devices, and high-frequency transistors. Due to its handling properties for high-frequency signals, this material plays a vital role in mobile phones, satellite communication systems, and radar technology. It is also commonly applied in LEDs, laser diodes, and solar cells because of its exceptional optical characteristics. Further, it is also a fundamental material in the sector of optoelectronic systems, including infrared light sensors and photodetectors due to its efficient light emission and absorption characteristics.
2. Gallium Nitride (GaN)
Gallium Nitride (GaN) is an III-V semiconductor with a wide band gap of around 3.4 eV. This makes it an ideal semiconductor material for several high-voltage, high-power, and high-frequency operations. GaN semiconductor is also famous for its heat resistance and ability to function at a high power level without degrading. It has high electron mobility and saturation velocity. This makes it a preferred choice for amplifying signals.
GaN is presently utilized in power electronics because of its wide bandgap and high power capabilities in applications such as power amplifiers, EV chargers, power convertors, and RF amplifiers. GaN is also combined in devices such as transistors and diodes, which are important components in the construction of 5G communications networks because of their ability to switch at high frequencies in order to transmit data. GaN is also applied in LED products, such as blue and white LEDs, in addition to being used in laser diodes in optical data storage projectors. GaN possesses a large breakdown voltage; therefore, radar communications are also part of GaN applications.
3. Ga₂O₃ (Gallium Oxide)
Ga₂O₃ (Gallium oxide) has a wide bandgap of about 4.9 eV and is a semiconductor material with a greater bandgap than GaAs and GaN. Due to its wide bandgap material properties, Ga₂O₃ can be used for high-voltage and high-temperature applications and is a potential material for electrical energy management devices and other power electronic devices as well. Ga₂O₃ also has excellent chemical stability and a high dielectric strength and is not liable to breakdown at extreme conditions. Ga₂O₃ is also highly transparent to ultraviolet light and can be utilized for ultraviolet applications.
Ga₂O₃ is also emerging in high-power electronics like power transistors, power diodes, and power switching materials in electric vehicles and renewable energy systems. The high breakdown voltage of Ga₂O₃ helps it to be used in power grids and solar power conversion systems where high efficiency in power conversion is required. Ga₂O₃ is also employed in UV photodetectors because it has the property to detect ultraviolet radiation. This is very important in the applications of UV communication systems.
Other Gallium Compounds
Beyond GaAs, GaN, and Ga₂O₃, several other gallium-based compounds are crucial in specialized electronic applications.
- Gallium Phosphide (GaP): Gallium phosphide has a direct bandgap of 2.26 eV. GaP is widely employed in the field of optoelectronics because of its property to emit light in the green/yellow regions. GaP is largely used in the preparation of LEDs for displays, traffic lights, and indicators. It is also used for solar cells as well as laser diodes.
- Ga₂Se₃ (Gallium Selenide) is a semiconductor material with high electron mobility and a direct band gap of 2.1 eV. Ga₂Se₃ has strong photoelectric properties. Ga2Se3 is applied as a photodetector material, solar cell material, and optical component because it has high light absorption ability. Ga2Se3 is also studied for photoelectrochemical devices.
- Gallium Sulfide: It is a wide bandgap semiconductor, hence a semiconductor. The chemical formula for gallium sulfide is Ga₂S₃. Additionally, it is an excellent conductor of electricity. Ga₂S₃ finds its major applications in photoelectric devices and solar cells. It also has possible uses in infrared sensors and thin-film transistors.
Summary Table of Key Gallium Compounds
|
Gallium Compound |
Bandgap |
Properties |
Primary Uses |
|
Gallium Arsenide (GaAs) |
1.42 eV |
High electron mobility, direct bandgap, thermal conductivity |
High-speed transistors, LEDs, solar cells, RF amplifiers |
|
Gallium Nitride (GaN) |
3.4 eV |
Wide bandgap, high thermal stability, high electron mobility |
Power amplifiers, 5G communication, blue LEDs, lasers |
|
Gallium Oxide (Ga₂O₃) |
4.9 eV |
Wide bandgap, high dielectric strength, UV transparency |
Power transistors, UV detectors, power conversion |
|
Gallium Phosphide (GaP) |
2.26 eV |
Direct bandgap, light emission in green/yellow |
LEDs, solar cells, laser diodes |
|
Gallium Selenide (Ga₂Se₃) |
2.1 eV |
High electron mobility, direct bandgap |
Photodetectors, solar cells, optical devices |
|
Gallium Sulfide (Ga₂S₃) |
3.2 eV |
High conductivity, chemical stability |
Photoelectric devices, infrared sensors, thin-film transistors |
For more gallium compounds, please check Stanford Electronics.
Conclusion
Gallium compounds, particularly Gallium Arsenide (GaAs), Gallium Nitride (GaN), and Gallium Oxide (Ga₂O₃), are vital to the advancement of modern electronics due to their exceptional electrical, thermal, and optical properties. These materials are extensively used in high-speed circuits, power electronics, LEDs, and lasers, as well as in emerging applications like 5G communications and quantum technologies.
Additional compounds such as Gallium Phosphide (GaP), Gallium Selenide (Ga₂Se₃), and Gallium Sulfide (Ga₂S₃) are also crucial in specialized applications, contributing to the broader scope of optoelectronics and photoelectric devices.
Reference:
[1] Electronics. (2025, December 22). In Wikipedia.