5G Networks & Semiconductor Revolution: What You Should Know
5G is more than the 'Next Generation' wireless network, but a game-changer. It boasts incredibly fast connectivity, lower latency, and the potential for a huge number of connections. However, there is a thing that is working in the background, facilitating the success of 5G. It is the 'Semiconductor' industry. It is hard to imagine a world where the promises of 5G can be met. It is time we take a look at how semiconductors are fueling the 5G revolution.
![]()
Semiconductors: The Pulse of 5G
When you hear 5G, you probably think of quicker downloads or better streaming functionality. Yet, what you don't see or understand are faster radios or different antennae used in 5G but rather what makes all this happen—the semiconductors in them all. Whether it's in your smartphone or 5G base station or in all the "things" that comprise the Internet of Things (IoT), semiconductors are what it's all about.
For instance, the 5G-enabled smartphone uses the latest System-on-Chip designs that incorporate all the required elements, such as processors and the 5G modem, into one chip. The System-on-Chip design targets the large data rates and low latency required by the 5G communication system while maintaining low power consumption, an important consideration when developing mobile products.
The Semiconductor Technologies Underpinning 5G
The demands of 5G require high levels of meet. This has driven a development in semiconductor technology. Below are a number of key elements pushing the development of semiconductor technology:
Gallium Nitride (GaN)
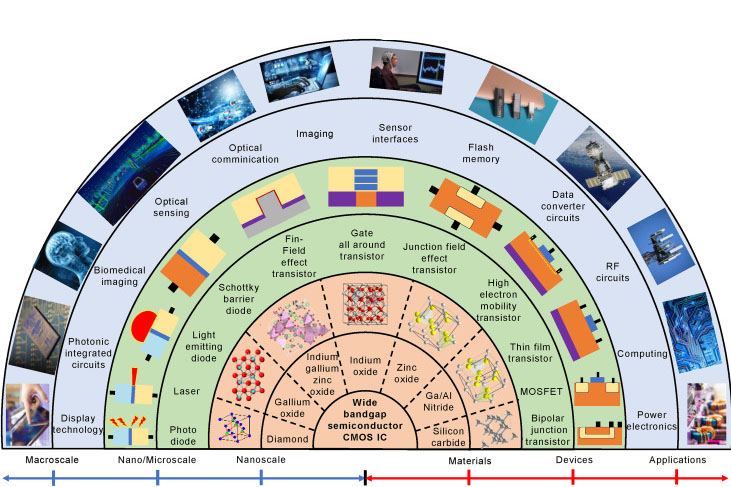
One of the stars of 5G infrastructure materials is gallium nitride. It is a wide band-gap semiconductor that has good performance characteristics at high frequencies as well as high powers. It is ideal for use in 5G base stations where high frequencies have to be processed without the use of cooling systems. GaN-based chips operate faster than the traditional Si-based ones.
Silicon Carbide (SiC)
Another wide band gap material that has gained popularity in 5G technology is Silicon Carbide. The thermal conductivity of SiC semiconductors allows them to work at higher power densities without heating up. This makes them a very important material used at the backbone of 5G technology. SiC semiconductors are more robust and work more efficiently.
High-End Packaging and Interconnection
As 5G chips become more powerful, they are expected to be of smaller size as well. New packaging solutions and innovations in SiP and 3D stacking are helping to pack multiple components into smaller and more power-efficient packages. Such innovations will help to integrate the powerful 5G solutions in mobile and IoT applications without affecting their performance and power efficiency.
The Challenges and Opportunities for Semiconductor Manufacturers
Although the future looks very promising with the advent of 5G, the semiconductor market has certain challenges in meeting the demand. Let's have a look at the key difficulties:
There is a need for a dramatic volume increase in the production of semiconductors to be utilized by the new 5G technology. From the smallest semiconductors used in mobile technology to the larger ones used in base stations, the need for high-quality and efficient semiconductors with advanced technology is unprecedented. The task at hand is to be able to meet this demand.
Power Efficiency
As the number of connected devices increases, power is becoming a key concern. Chip manufacturers are challenged with the need to develop chips that are capable of supporting high data rate transmission and power efficiency simultaneously. Chip manufacturers are, therefore, faced with the challenge of reducing power consumption by their chips.
Supply Chain Disruptions
The global semiconductor supply chain has experienced some disruptions over the years. These disruptions range from the production of smartphones to the deployment of 5G technology networks. A delay in the availability of critical or technically important material can cause a setback in the deployment of 5G networks. These are some pressures that the semiconductor manufacturers are currently facing.
Role of 5G Technology
The emergence of 5G has begun to change the semiconductors industry in a radical manner. As and when wireless communication technology upgrades, semiconductors develop along with it. Here's what is happening in the semiconductors industry due to 5G:
The Rise of Networked Devices
With the vast capacity offered by 5G for supporting an almost limitless number of devices, the Internet of Things (IoT) is poised to go explosive. Starting from IoT-based smart homes to internet-linked vehicles, the requirement for semiconductors supporting thousands of connections simultaneously is in great demand. This has prompted semiconductor manufacturers to develop dedicated chips for IoT applications ranging from self-driving vehicles to smart cities.
Edge Computing
5G has ultra-low latency capabilities that are powering the ability to compute in real time. This makes it possible to do calculations closer where the data is being created. Semiconductors play a crucial role in the transformation where they are powering the devices that allow the calculations to happen in areas such as the factory or the self-driving car.
AI & Autonomous Systems
The speed and latency offered by 5G are critical for the adoption of artificial intelligence and autonomous technologies, which require real-time executions of their processes. Artificial intelligence in manufacturing, autonomous vehicles, and other technologies are utilizing semiconductors as the backbone in decision-making systems, which instantly respond to changes in the environment surrounding them.
The Road Ahead: What's Next for 5G and Semiconductors
As 5G technology continues to expand its reach throughout the world, the semiconductor industry will play a crucial role in its success. The coming years will only bring about further innovation in the technology associated with semiconductors, with new materials, new processes, and new applications being made possible by 5G technology.
Looking forward, innovations such as 6G technology are set to push the semiconductor industry to great heights, requiring even more rapid and efficient semiconductors capable of supporting the exponential increase in connectivity, data, and applications.
But for now, the future is 5G, and this is a huge leap forward. It is much more than faster download speeds. It is the transformation of industries, new possibilities, new services, and new horizons yet to be imagined. But the backbone of this, the unsung heroes, is semiconductors.